
50 Facts for 50 Years: Promoting Openness, Transparency and Public Access
Post filed in:
This month we are celebrating the 50th anniversary of the Federal Advisory Committee Act. To learn more about FACA and help celebrate 50 years of diverse thought and action, this blog series will reveal 50 facts for 50 years. Find the first and second installment here, then come back and read 23 through 34 focused on the FACA program’s early evolution promoting openness, transparency, public access and instituting best practices.
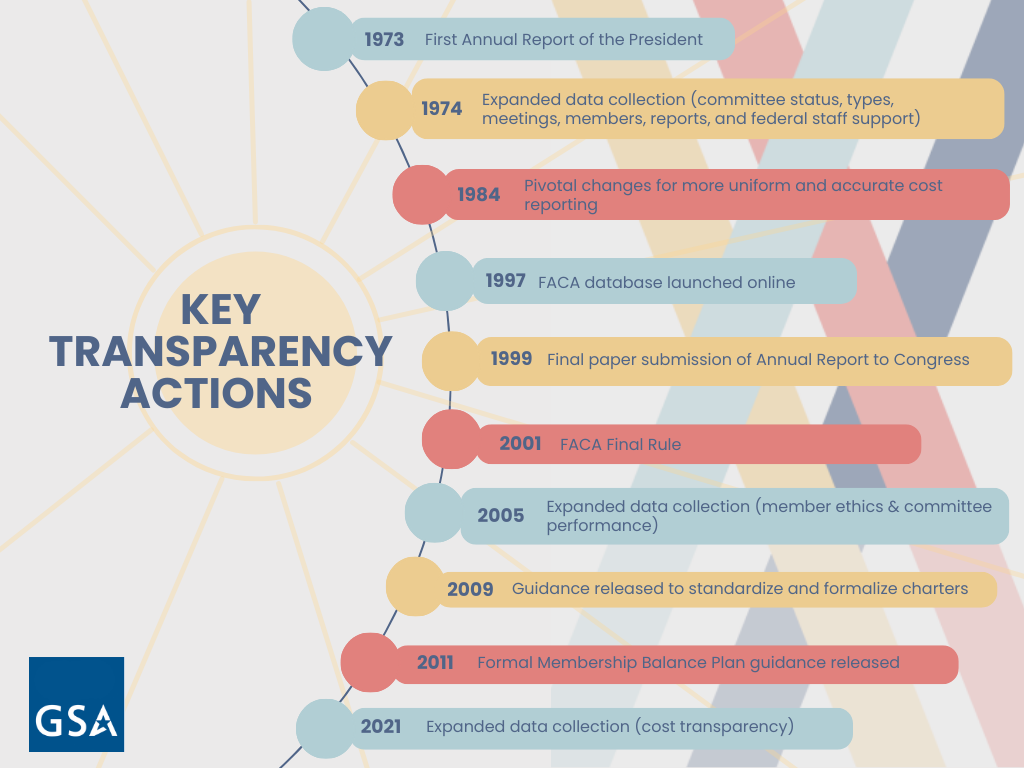
24. In the late 1980s, GSA worked with the Executive Office of the President to evaluate the implementation of FACA. It resulted in:
- A new internal governmentwide FACA training program, supported by agency instructors.
- GSA establishing the Interagency Committee on Federal Advisory Committee Management.
25. By 1993, the FACA program started the shift from slow, labor intensive paper reporting to digitizing these reports on the internet. The world wide web became accessible to all, and in the spirit of transparency, GSA posted summary committee information and committee documents on a gsa.gov web page!
26. In this technological backdrop, GSA began developing a new Internet-based governmentwide shared system for agencies to input their FACA data. By fiscal year 1997, all data was entered online. This marks the birth of the online FACA database.

27. The 1997 Annual Report of the President on Federal Advisory Committees not only marked the 25th anniversary of FACA but predicted, “during its second quarter-century, FACA will continue to play an important role in fortifying the use of advisory committees as a uniquely American approach toward collaboration.” Indeed, this commitment lives on at FACA’s 50th Anniversary.
28. While the FACA community was advancing transparency through the FACA database, GSA and its agency partners expanded opportunities for public access and participation by encouraging the use of videoconferencing and toll-free phone lines. This also reduced committee operating costs. The focus on expanding public access under FACA paved the way for the 2001 FACA regulation.
29. On July 19, 2001, after collaborating with agency partners, GSA issued the Federal Advisory Committee Management Final Rule.

30. The 2001 Final Rule amended language to ensure that agencies adequately planned and made it easier for the public to witness and provide input into the committee process by:
- Highlighting that the Act applied to both physical and virtual meetings (including teleconferences, videoconferences, the internet or other electronic media).
- Providing for adequate public access to advisory committee meetings held electronically in whole or in part.
31. Since 2009, GSA has provided formal Guidance for Preparing Federal Advisory Committee Charters to help executive branch agencies comply with FACA’s requirements when establishing federal advisory committees. Charters help the public understand the committee’s purpose, objectives, and other aspects of a committee’s operation.
32. Since 2011, GSA has provided Membership Balance Plan Guidance to provide a framework for committee membership balance. FACA mandates that federal advisory committees be fairly balanced in the points of view represented by the members and the functions to be performed by the advisory committee, yet leaves it to the discretion of each agency on how to do this.
33. FACA through numbers! The graphics below depict the dynamic nature of the program and how it continues to change through the years.
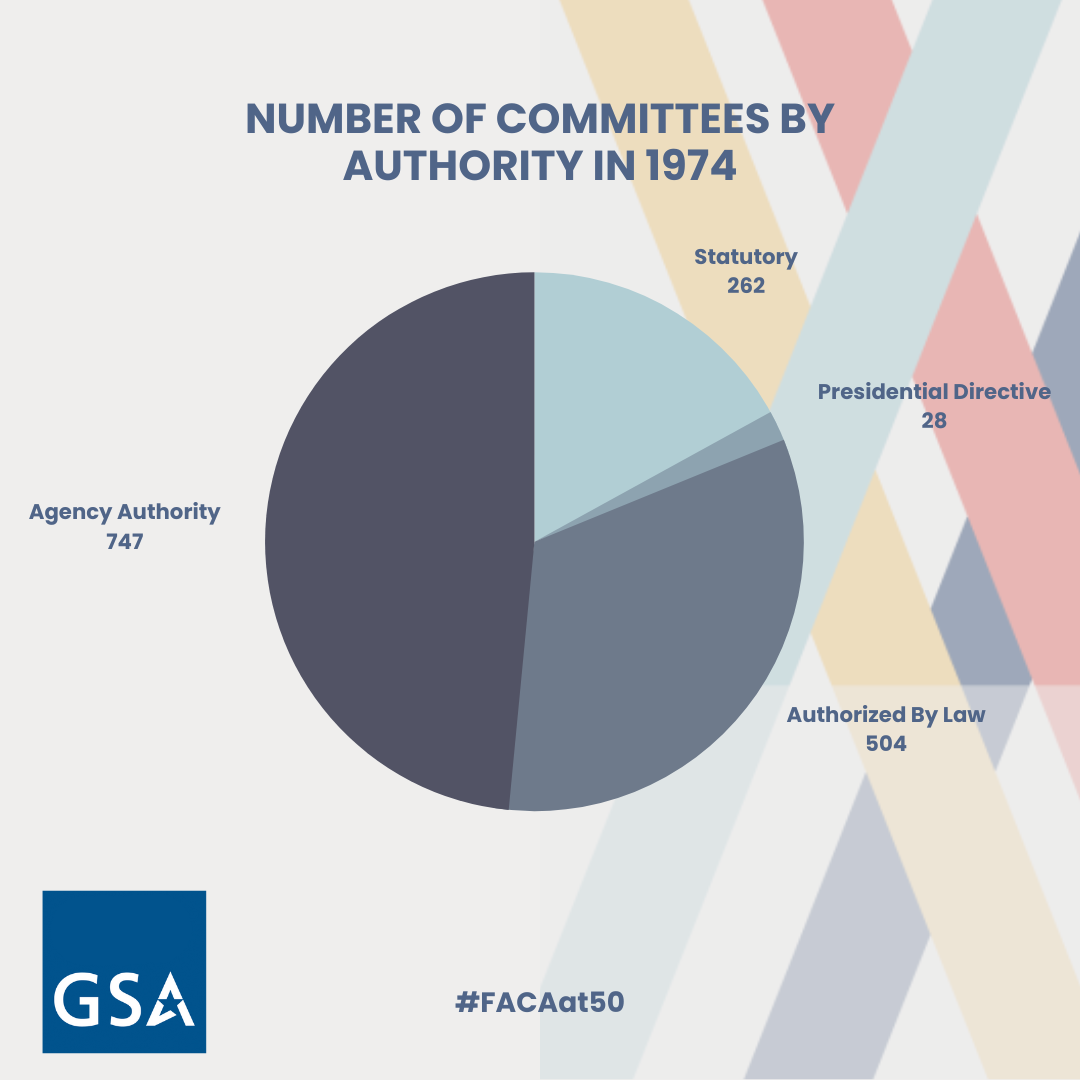
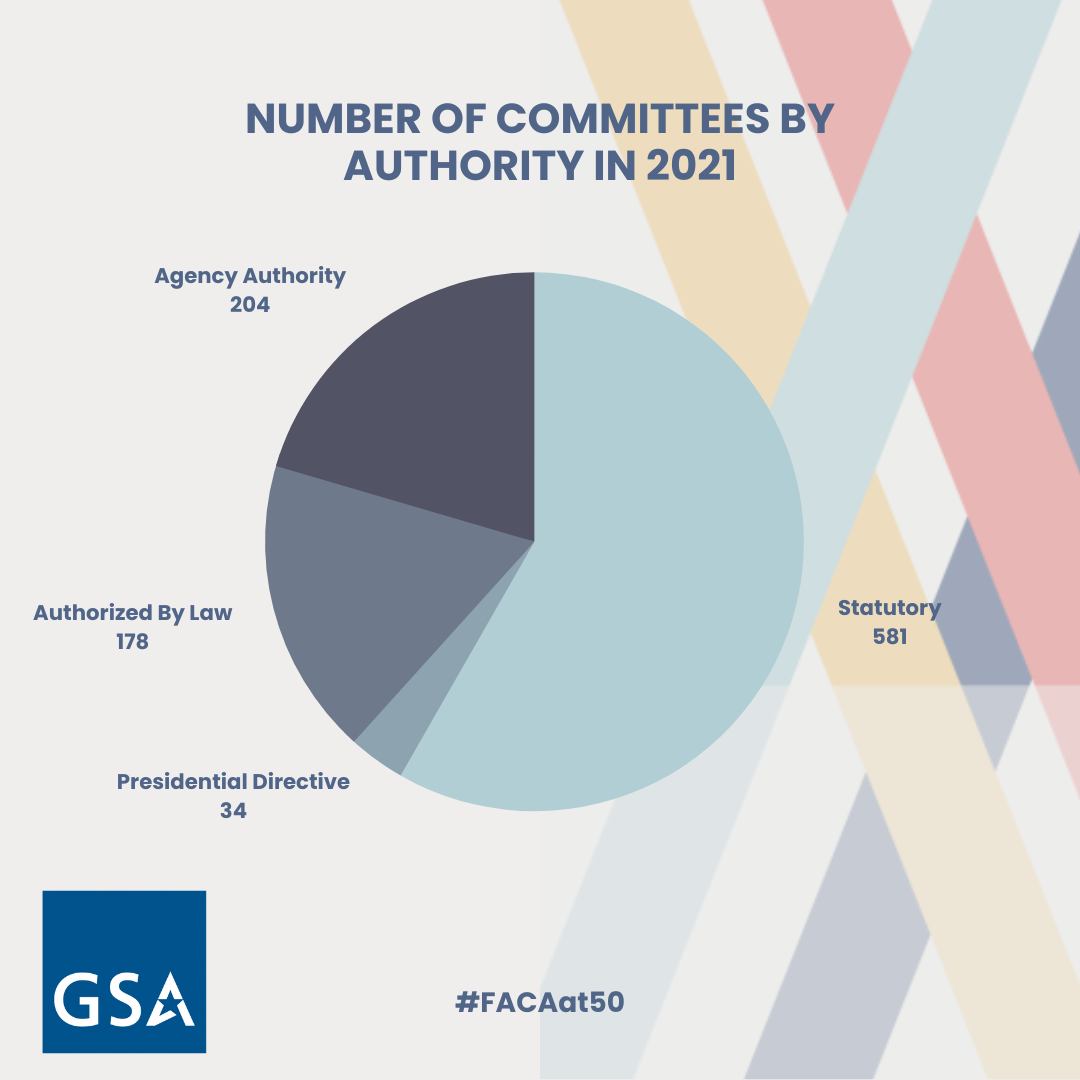
34. Did you know? GSA’s Committee Management Secretariat is the oversight office for FACA who works closely with its agency partners in FACA. 
Stay tuned for the stories agencies have to tell about the diverse work and impact their committees have on the lives of the American people in our next blogs.
 U.S. General Services Administration
U.S. General Services Administration
