Trusted Internet Connections is a federal cybersecurity initiative intended to enhance network and data security across the Federal Government. The Office of Management and Budget, the Department of Homeland Security Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency, and the General Services Administration oversee the TIC initiative through a robust program that sets guidance and an execution framework for agencies to implement a baseline boundary security standard. Originally established in 2008, the initial versions of the TIC Initiative sought to consolidate federal networks and standardize perimeter security for the federal enterprise.
On September 12, 2019, OMB released M-19-26 with the goal of “Updating the Trusted Internet Connections (TIC Initiative)”. M-19-26 provided an enhanced approach for implementing the TIC initiative that enabled agencies with the increased flexibility to leverage modern security capabilities, while also establishing a process for ensuring the TIC Initiative is agile and responsive to advancements in technology and rapidly evolving threats. CISA branded this evolution of the program as TIC 3.0 and has since developed Core Program and Use Case Guidance to support and navigate the program’s paradigm shift. The TIC 3.0 program updates have modernized and expanded the original version of the initiative to drive security capabilities to better leverage advances in technology as agencies decentralize their network perimeters or system boundaries to better support the remote workforce and the continued adoption of cloud service provider environments.
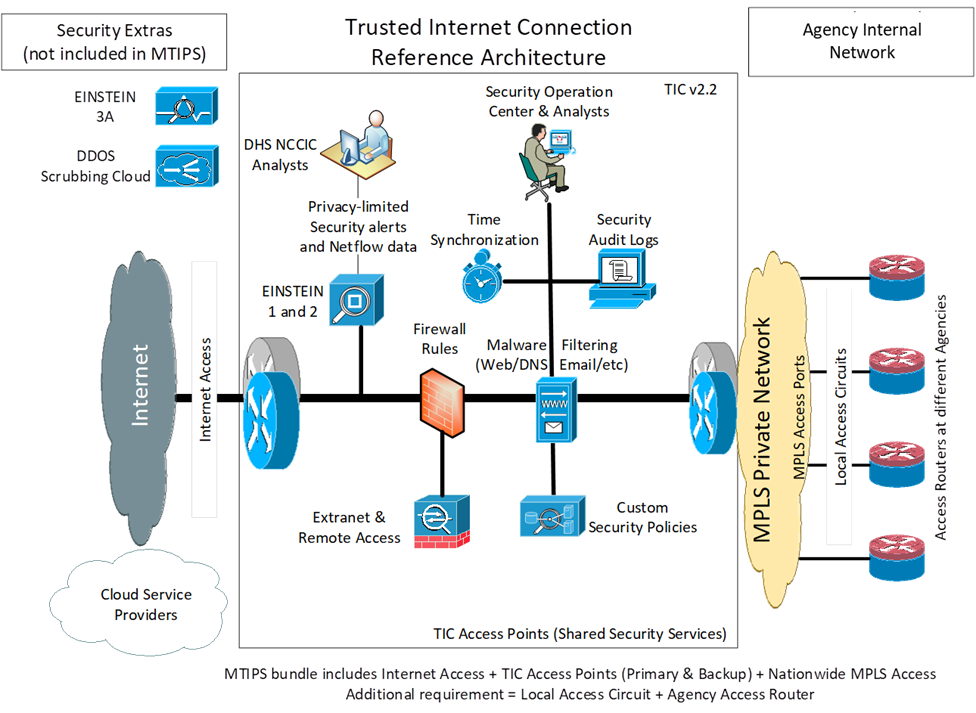
GSA managed trusted internet protocol services — traditional TIC solution
GSA Managed Trusted Internet Protocol Service is an orderable solution for the CISA TIC 3.0 Traditional TIC Use Case [PDF] modeled after the perimeter-based internet security paradigm. MTIPS is offered as a managed security service through the GSA Enterprise Infrastructure Solutions contract.
Agencies may leverage MTIPS along with other EIS managed or cloud services to adhere to CISA’s TIC 3.0 guidance.
GSA and DHS jointly developed the requirements for the MTIPS Trusted Internet Connection Access Provider service. The high-level working parts include:
- Internet access
- Hosted EINSTEIN enclave (a computer network intrusion detection system)
- A Security Operations Center
- MTIPS transport
The MTIPS SOC monitors all information exchanged with external networks to protect agency traffic. The MTIPS transport serves as a group network for the TIC portal, insulating an agency’s internal network from the Internet an other external networks.
Each MTIPS partner solution undergoes the Assessment and Authorization (A&A) process and is issued an ATO from the GSA at the FISMA High Level. The MTIPS contractor is required to identify and route government traffic through a secure CISA EINSTEIN Enclave for processing by the latest generation of EINSTEIN capabilities.
The MTIPS industry partner provides and supports two (2) components associated with the MTIPS service:
- TIC Portal (TIC Access Points) - (These must be closely monitored by an integral MTIPS Security Operations Center to protect agency network traffic.)
- Transport Collection and Distribution (MTIPS Transport) — (This serves as a “collection” network for TIC physical or virtual portal connectivity insulating an agency’s internal network from the Internet and other external networks.)
Due to the physical implementation nature of the Tradition TIC use case, prescribed EIS CLINs for ports and access methods as well as additional features are defined in EIS for MTIPS.
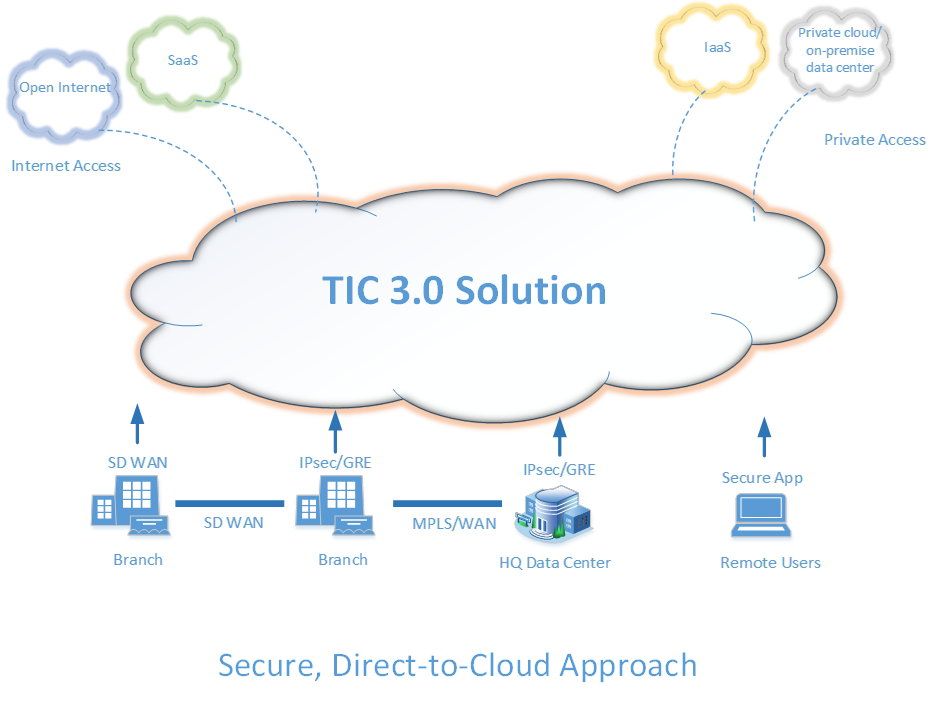
GSA solutions for other TIC 3.0 use cases
GSA has contract and schedule solutions to deliver on agency requirements for the Branch Office, Remote User, Cloud and other TIC 3.0 Use Cases.
Solutions for these TIC use cases are available from the Enterprise Infrastructure Solutions contract using one or more of the following services:
- Managed Security Service Trusted Internet Connections Service.
- SD-WAN Service as fully managed, co-managed, or do-it-yourself implementations.
- Broadband Internet Service and/or Internet Protocol Service.
- Secure Access Service Edge, Cloud Access Security Broker and other security services may leverage the EIS Managed Security Service and/or Software as a Service cloud services.
- Virtual Private Network Service for traditional MPLS wide area networking while leveraging the Cloud Service Provider Connection feature for direct connectivity to cloud resources.
For agency-specific TIC customized solutions and/or when additional related network security services are required agencies may leverage the EIS Managed Security Service (MSS) Trusted Internet Connections Service (TICS). MSS TICS may be leveraged to supplement capability gaps between TIC 2.2 services like MTIPS or other Traditional TIC access points and the TIC 3.0 security capabilities. MSS TICS may also be leveraged in combination with other EIS services as needed to address other TIC and cybersecurity requirements an agency may have.
Resources
Contact us
 U.S. General Services Administration
U.S. General Services Administration